Question:
What effect does a dead time in the actual value of the load encoder have on the speed comparison in Extended Safety?
Answer:
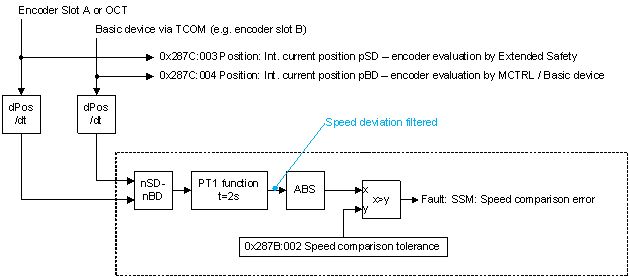
In Extended Safety, a speed difference is formed from the motor encoder speed and the load encoder speed. If this difference exceeds the Tolerance speed comparison threshold, the SSM: Error speed comparison is signaled.
Before the comparison, a possible noise of the speed difference is minimized by PT1 filtering.
A dead time in the load encoder position results in a difference being formed between speeds that were sampled at different times. A current motor encoder speed is therefore compared with a load encoder speed,
which corresponded to the actual load velocity x ms ago.
The effect is a speed-dependent difference between the two speeds.
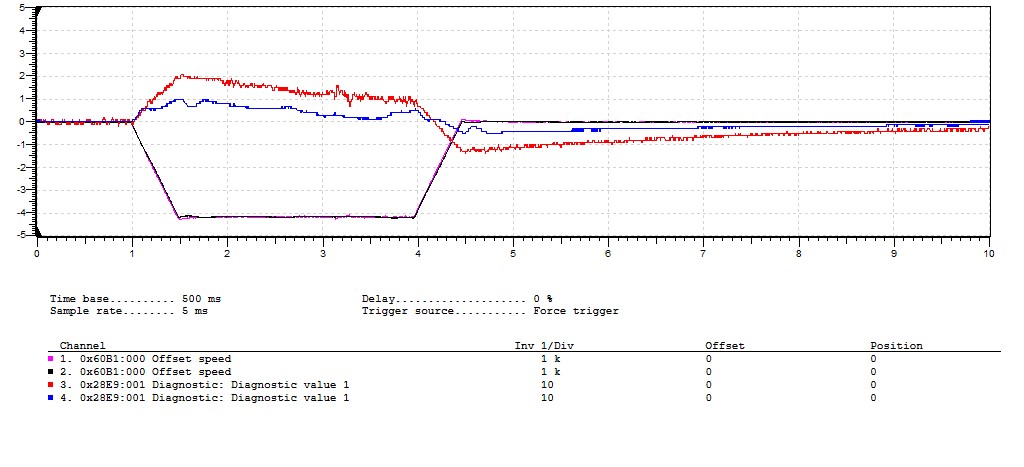
The figure below shows the speed deviation filtered from two SSI linear encoders of different types.
- The oscilloscope recording is stitched together from two individual recordings with the same motion and kinematics.
- With encoder type A (channel 1; red) a dead time of 12-14 ms is effective in the position detection.
This results in a maximum speed deviation filtered = 20 rpm (at approx. n_motor = 4000 rpm). - For encoder type B (channel 2; blue ), approx. half the dead time of encoder type A is effective.
- Note: The signal Speed deviation filtered cannot be oscillated with the current firmware version of the Extended Safety. Here, an internal interface was only used for the test.