Question:
How can a positioning function be realised in the 9300 EK servo cam?
Answer:
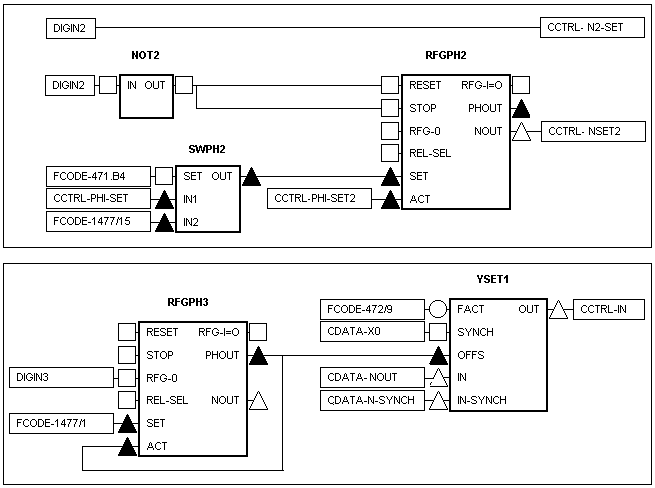
In applications with cam drives a positioning function is often required, e. g. for setting up the drive or as superposition to the motion profile. In the firmware versions from V2.x on profile generators are available as function blocks RFGPH2 and RFGPH3, in order to realize a simple positioning function based on a created positional deviation.
The detailed function of the function blocks RFGPH2 and RFGPH3 is described in the manual of the 9300 EK servo cam.
The function block interconnections in the figures below show an application example for an
overriding positioning and an example for a
superimposed positioning to the cam.
Overriding positioning:
The positioning, overridden from the cam via function block RFGPH2, is to be realized by the additional control via function block CCTRL.
The function is applied e. g. for mounting, preparing, cleaning a machine or a machine module.
- The drive is separated from the cam while the assignment to the curve pulse is maintained (in the example via digital input E2).
- Also during positioning the set position of the cam is available in function block CCTRL (signal output CCTRL-PHI-SET).
- Alternatively the position overridden from the cam can be determined (in the example via the free code C1477/015 in [s_units]).
- The drive can be repositioned to the cam's set position via the ramps and speed set in function block RFGPH2.
The function is also suitable for overriding the drive from the cam position to a control signal and to move it to a save position outside the movement area of the cam.
Superimposed positioning:
The positioning, superimposed to the motion profile in the example via function block RFGPH3, can be realized directly by the connection of an angle offset to function block YSET1. The angle offset is rounded via ramp function RFGPH3.
The function is applied e. g. for mounting/manual positioning, home position, trimming the axis of a machine or a machine module.
- Positioning of the angle offset (in the example the free code C1477/001) acts additively to the running motion profile.
- In the shown example a connection/disconnection is executed via the digital input E3.
- Cam movement and positioning are superimposed via the set ramps in the drive.
- The angle offset generates a shift of the motion profile with reference to the mechanics of the machine (y axis).